Vitreous Hemorrhage
Overview
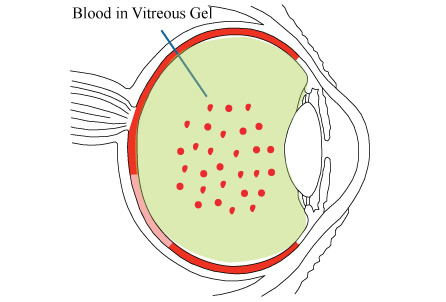
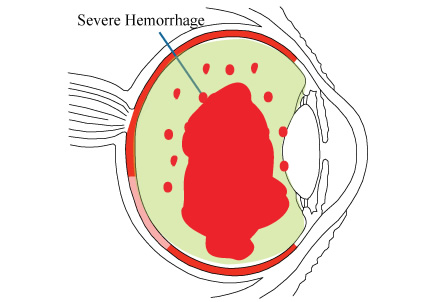
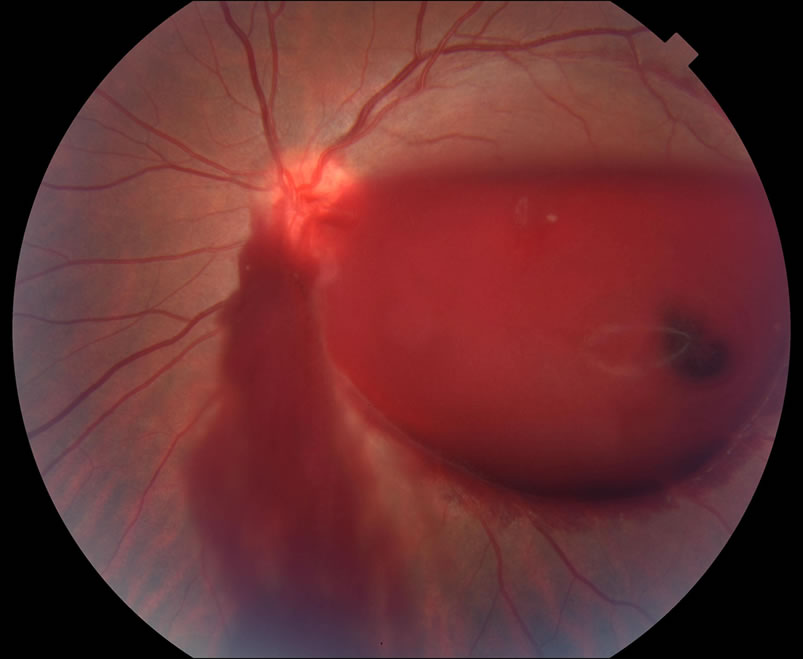
The vitreous gel inside the eye is normally mostly clear. Some of the collagen fibers inside the vitreous gel can start to mature with age and turn into little clumps or strands, which can be visible as floaters. They are noticeable especially when looking at a bright background like a white computer screen or the blue sky. If you develop a vitreous hemorrhage, you may notice sudden appearance of more floaters in your vision. If the hemorrhage is severe, the entire vision can turn dark. There are many conditions that can cause a vitreous hemorrhage. Depending on the cause, different treatments may be needed. If you think you have develop a vitreous hemorrhage, you should see a retina specialist promptly.
Vitreous Hemorrhage
Causes
A hemorrhage in the vitreous gel can develop from a bleeding vessel in the retina. Sometimes the bleeding can come from under the retina or from the front of the eye. There are many possible causes. The most common cause of a vitreous hemorrhage is posterior vitreous detachment, where the vitreous gel contracts with age and the pulling forces of the gel rupture a tiny blood vessel in the retina. Other causes include:
- Retinal tear or detachment
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Retinal vein occlusion
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Retinal arterial macroaneurysm
- Ocular trauma
- Sickle cell retinopathy
- Intraocular tumor
Symptoms
Patients with vitreous hemorrhage may notice:
- A sudden, significant increase in the number and size of floaters
- Vision loss
- Blurry, cloudy or hazy vision
- Flashes of light
When symptoms occur, you should see a retina specialist promptly.
Treatment
The type of treatments used to treat a vitreous hemorrhage depends on the cause and severity of the vitreous hemorrhage. If the vitreous hemorrhage is associated with a more threatening condition like a retinal detachment, surgery may need to be performed. Treatment is tailored to the individual patient situation and may include:
- Monitoring
- Laser treatment
- Cryotherapy
- Intravitreal injections
- Vitrectomy surgery